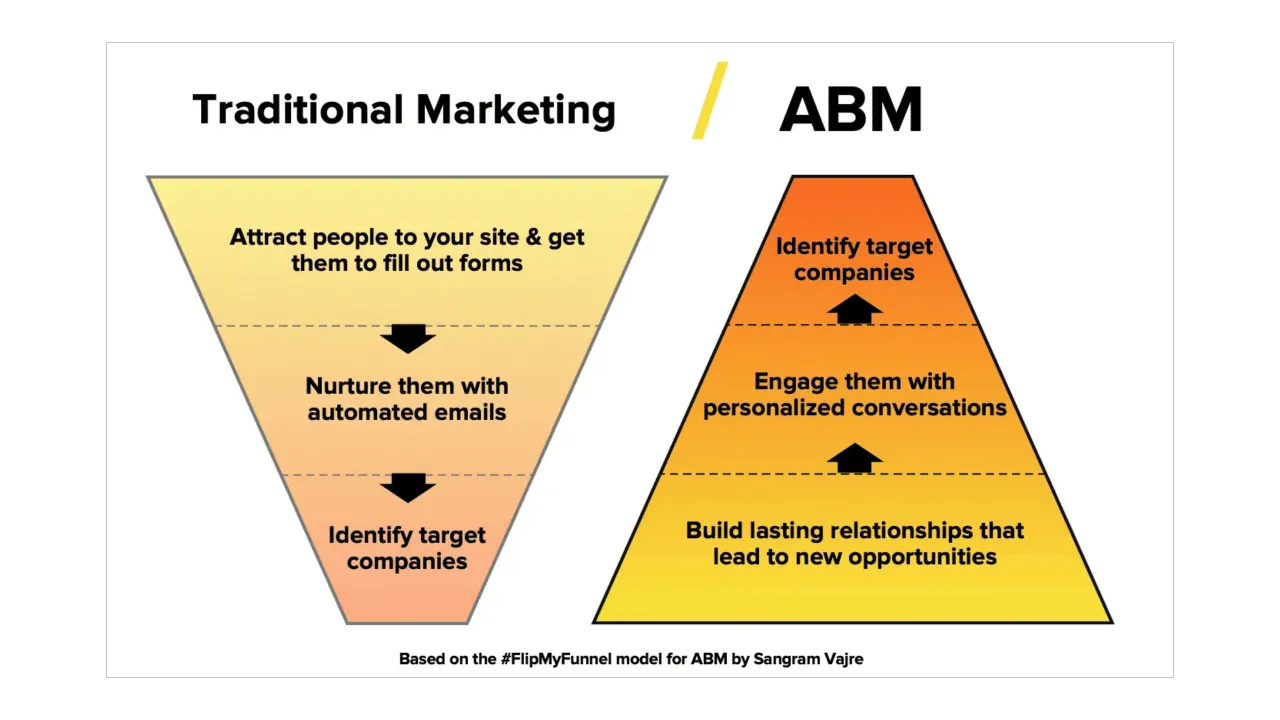
Success in the industrial engineering & manufacturing space, depends on precision, efficiency, and alignment. The same is true for implementing Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategies. A robust ABM strategy must begin with clearly defined goals and objectives that align seamlessly with overarching business objectives. These goals not only provide direction but also ensure every marketing effort is optimized to deliver measurable value.
This blog delves into the process of setting ABM goals, aligning them with business objectives, and identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure success—all tailored to the unique challenges and opportunities within the industrial engineering and manufacturing sectors.
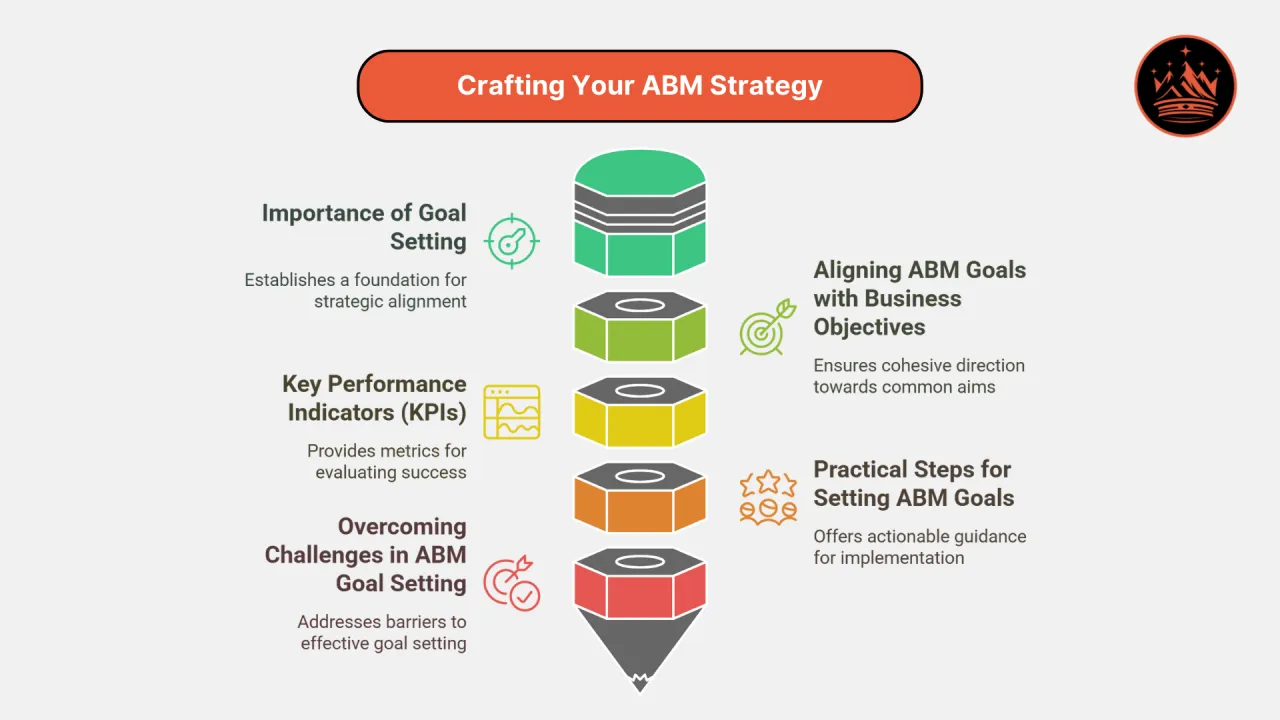
The Importance of Goal Setting in ABM
ABM is a resource-intensive strategy, requiring precise targeting and personalized campaigns to high-value accounts. Without clearly defined goals, even the best ABM campaigns risk losing focus, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities. Goals serve as the foundation for:
- Guiding Strategy: Providing clarity on what the ABM initiative aims to achieve.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring time, budget, and talent are directed toward high-impact activities.
- Performance Measurement: Establishing benchmarks for success and areas of improvement.
Aligning ABM Goals with Business Objectives
To maximize the impact of ABM, its goals must align with broader business objectives. Here’s how industrial manufacturers can achieve this alignment:
1. Understand Business Objectives
Business objectives in the industrial sector often revolve around:
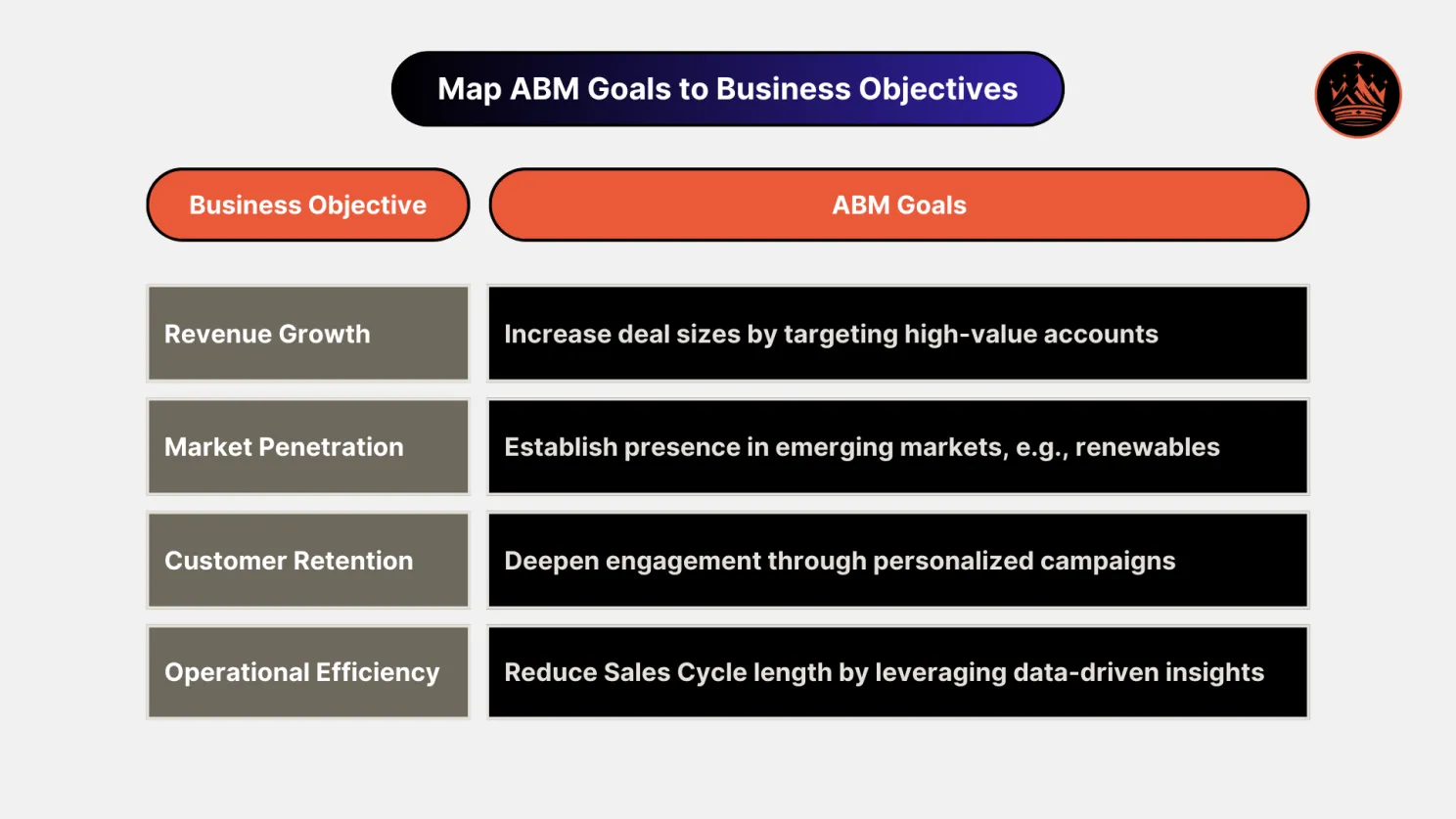
- Revenue Growth: Securing high-value contracts with long-term potential.
- Market Penetration: Expanding into new geographies or industries.
- Customer Retention: Strengthening relationships with key accounts to foster loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining marketing and sales processes to reduce cost-per-acquisition.
2. Map ABM Goals to Business Objectives
For each business objective, identify corresponding ABM goals. Examples include:
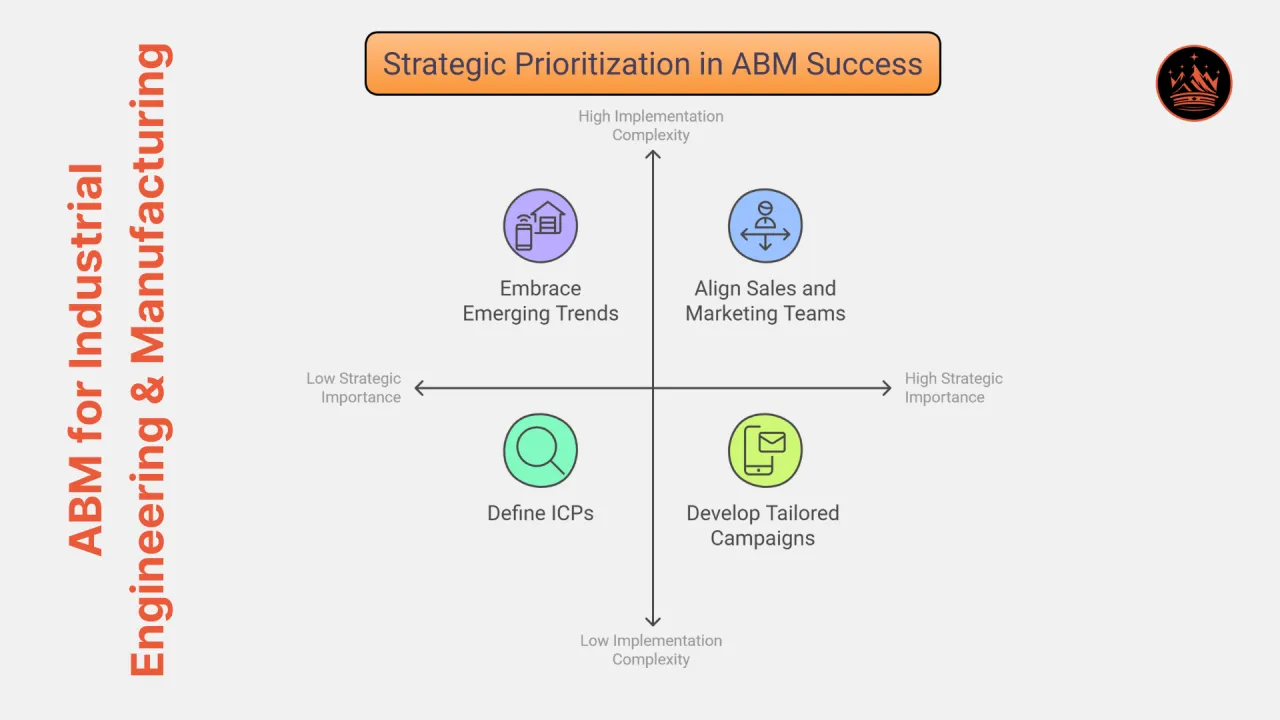
3. Prioritize High-Impact Goals
Not all goals carry equal weight. Industrial manufacturers should prioritize goals that:
- Have the most significant impact on revenue
- Address urgent market opportunities
- Align with internal capabilities and resources
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Success
Defining the right KPIs is critical to evaluating the effectiveness of your ABM strategy. For industrial engineering manufacturers, these KPIs should reflect the nuances of long sales cycles, complex buying committees, and high-value deals.
1. Account Engagement Metrics
Measure how effectively your campaigns are engaging target accounts. Key metrics include:
- Content Engagement: Page views, whitepaper downloads, webinar attendance, etc.
- Time Spent: Duration spent interacting with your website or materials
- Repeat Visits: Frequency of visits from target accounts
2. Pipeline Metrics
Track the progression of target accounts through the sales pipeline:
- Qualified Accounts: Number of accounts that meet your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) criteria
- Opportunities Created: Target accounts progressing to active opportunities
- Pipeline Value: Total value of opportunities generated from ABM Campaigns
3. Revenue Metrics
Revenue-focused KPIs reflect ABM’s impact on the bottom line:
- Deal Size: Average value of closed deals from ABM Campaigns
- Win Rate: Percentage of targeted accounts converted into customers
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Long-term revenue potential of accounts acquired through ABM
4. Collaboration Metrics: Driving Unified Efforts
For industrial manufacturing businesses, success in ABM relies on sales and marketing teams working together seamlessly. Collaboration is the engine that ensures the right message reaches the right accounts at the right time. While direct revenue impact is the ultimate goal, tracking how well these teams align can shed light on potential bottlenecks in the buyer’s journey.
Here’s how collaboration contributes to measurable outcomes:
- Consistent Follow-Ups: Monitor how quickly leads from marketing are acted upon by sales. A timely follow-up is often the difference between a converted lead and a lost opportunity.
- Aligned Targeting: Assess how often sales and marketing agree on the list of high-priority accounts to target. This ensures that both teams are working on the same high-value opportunities.
- Actionable Feedback: Ensure regular check-ins between teams to discuss what’s working and what isn’t, enabling a cycle of continuous improvement.
Why This Matters:
When sales and marketing work in sync, the results are tangible: faster deal cycles, fewer missed opportunities, and stronger engagement with decision-makers. While these metrics aren’t about vanity, they highlight areas where alignment directly supports ABM outcomes like increased pipeline velocity and deal sizes.
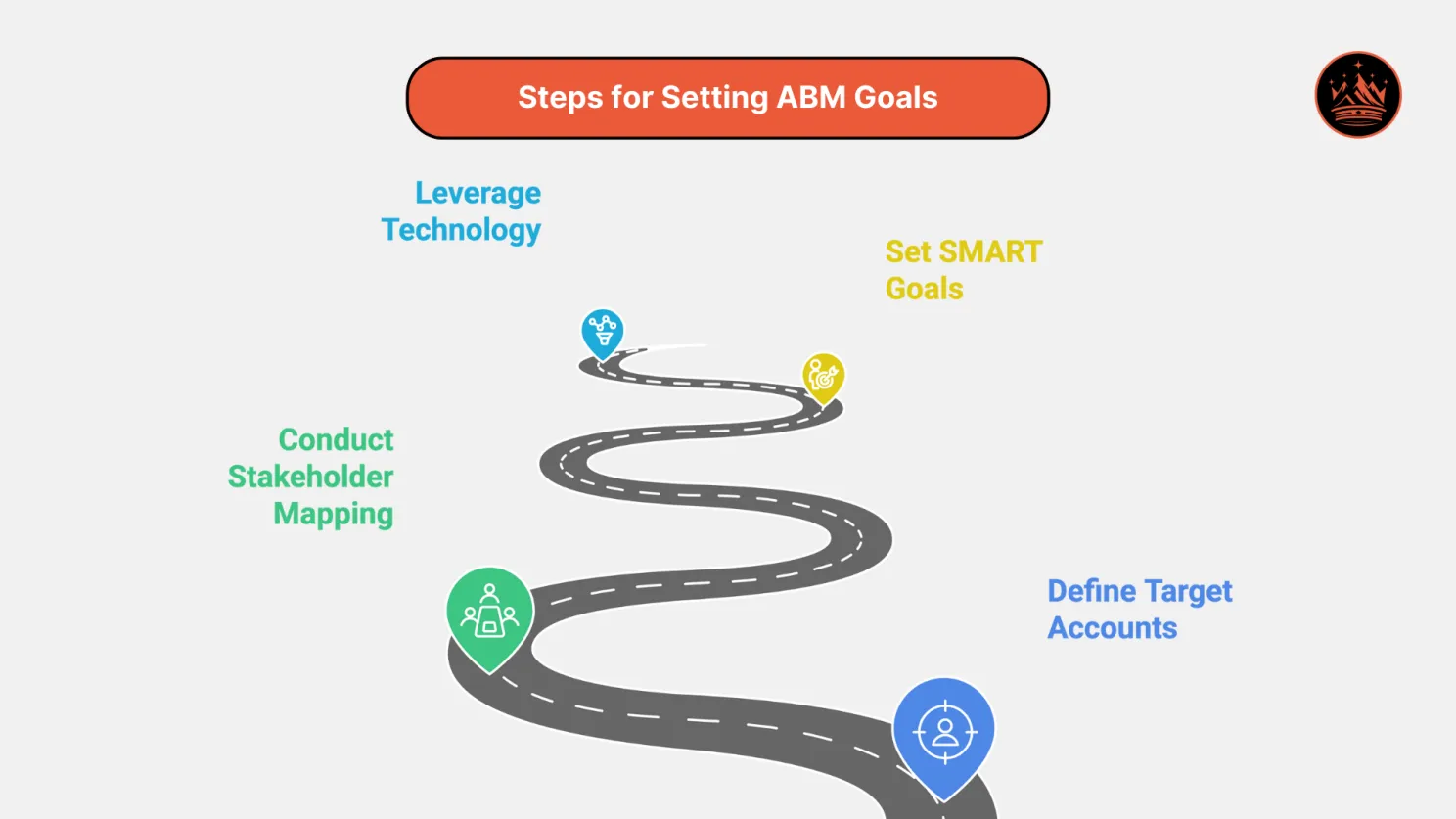
Practical Steps for Setting ABM Goals
1. Define Target Accounts
Identify the high-value accounts that align with your business objectives. Use tools like CRM platforms, intent data, and industry reports to refine your selection.
Example: A manufacturer of industrial pumps might target pharmaceutical companies expanding their production facilities.
2. Conduct Stakeholder Mapping
Understand the buying committee within each target account. For industrial engineering manufacturers, this often includes engineers, equipment operators, procurement officers, and C-suite executives.
3. Set SMART Goals
Goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound. Examples include:
- Specific: Increase engagement with target accounts by 25% within six months.
- Measurable: Generate 10 new opportunities from Tier-1 accounts.
- Achievable: Focus on five high-value accounts per quarter.
- Relevant: Align campaigns with the company’s market expansion strategy.
- Time-Bound: Close three new deals worth $50,000+ within 12 months.
4. Leverage Technology
Use advanced ABM platforms and tools to monitor progress. Integrate CRM systems, marketing automation, and analytics platforms to track KPIs in real-time.
Challenges in Setting ABM Goals and How to Overcome Them
1. Misaligned Sales and Marketing Teams
Solution: Foster collaboration through regular joint planning sessions and shared KPIs.
2. Lack of Data Transparency
Solution: Invest in integrated platforms that consolidate data across sources and across departments.
3. Overly Ambitious Goals
Solution: Break goals into achievable milestones and adjust based on performance data.
4. Evolving Market Dynamics
Solution: Regularly revisit and update goals to reflect changing industry trends.
Example Case Study: Successful ABM Goal Setting
Scenario: A company specializing in automated welding systems wants to penetrate the wind energy sector.
Goals Set:
- Identify 10 high-value wind turbine manufacturers
- Engage decision-makers through tailored campaigns showcasing operational efficiencies
- Secure new contracts within 12 months
Results: By aligning ABM goals with business objectives, the company acquires new business, reduces sales cycle time by 20%, and establishes strong relationships with key accounts.
Setting and aligning ABM goals with business objectives is a critical step for industrial engineering and manufacturing businesses seeking to maximize their marketing ROI. By leveraging KPIs, fostering collaboration between sales and marketing, and continuously refining strategies, manufacturers can transform their ABM efforts into a powerful driver of revenue growth.